This Week in Life Science #3

Well its been almost 3 weeks since I’ve updated thanks to holidays and a pesky illness but as per usual it has been an incredibly busy and promising time across the science world. From termite poop to diamond-encrusted teeth to ‘black holes’ at sea, there has been no shortage of scientific progress announced recently. As usual, all source material is cited, just follow the links provided in each title. Most have additional videos and graphics. I’d recommend checking out Carl Harts story ‘The Rational Choices of Drug Addicts’ for a drastically different perspective on the world of addiction to the one the media often portrays.
French Progress in the reversal of Dwarfism
A French research paper published last week has shown major progress in reversing the effects of dwarfism. Mice affected by the condition known as achondoroplasia, the genetic mutation responsible for the vast majority of human cases of dwarfism, were injected with a protein over the course of three weeks which caused therm to grow fully and also prevented some of the uncomfortable side effects of this condition.
Termite Poop May be Essential to the Discovery of new Antibiotics!
Termites use their own poop as building material and as disgusting as that sounds (well, they are insects) this has actually proven to be one of the keys to their success as a species. The feces has a natural antibiotic property which suppresses pathogens which enter the nest. This is one of the reasons why termites have proven difficult to suppress by biological means,. but also could herald the discovery of new antibiotics for us above ground-dwellers.
We have a whole range of scientific opportunities here at Life Science. Check out whats hot right now.
Sleep is Shown to help Overcome Our Fears
Scientists at Northwestern University have published the results of a study which touts the power of sleep as a potential conqueror of our fears. The scientists first induced fear in the test subjects by shocking them with electricity while showing them a picture of a face. They then released an odour which conditioned the patients to associate the smell with the fear. This smell was then released while the patient slept to trigger fear memories which the patients could process without a conscious confrontation of the fear.
The Rational Choices of Drug Addicts
Professor of psychology at Columbia University, Carl Hart, conducted an experiment where drug addicts were offered a choice between drugs and cash or vouchers. The results showed that when given this choice, users almost always chose the money and vouchers when the amount of drugs on offer was small. It was only when a large amount of drugs were on offer that they were taken. These findings are important for challenging the stereotype of addicts as ‘helpless.’ The perception of drugs addictiveness is being challenged too, with Hart stating that Eighty to 90 percent of people who use crack and methamphetamine don’t get addicted […] and the small number who do become addicted are nothing like the popular caricatures.” The full article is well worth checking out as is the accompanying video.
Newly-Discovered Structure Blows Particle Physics Wide Open
A structure has been discovered which has blown open a whole new perspective on the world of particle interactions, and challenges the notion that space and time are fundamental components of reality. The jewel-like framework, known as an amplituhedron, can be used to calculate interactions that used to take hundreds of pages – and were impossible on early computers – in just one single term.
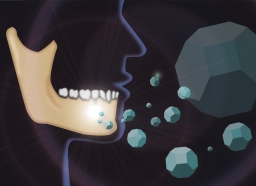
Are Nano Diamond Encrusted Teeth the Future of Dental Implants?
Diamonds 4-5 nanometers small could revolutionise the use of dental implants, promoting bone growth and improving durability. A collaborative effort between UCLA school of dentistry and the Japanese research outfit The NanoCarbon Research Institute may have found a way to use nano diamonds to improve bone growth and combat osteonecrosis, a degeneration of bone caused by bad blood flow.
New Transitional Phase of Water Discovered
Research conducted at the University of Arkansas has shown that water when cooled to an extremely low temperature enters a liquid-liquid phase at 207 Kelvin or about -66 Celsius. this liquid-liquid transition is important for understanding basic processes during cryoprotection or the preservation of organic tissues during cryogenic freezing so they can be thawed out again safely.
We have a whole range of scientific opportunities here at Life Science. Check out whats hot right now.
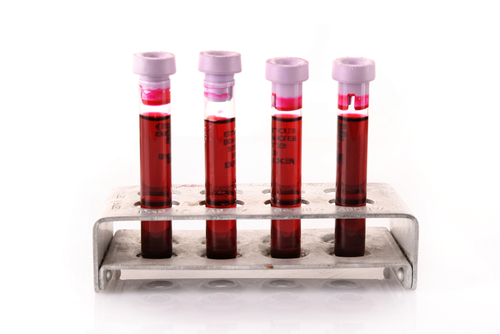
Rapid Blood Test Can Tell the Difference Between Viral and Bacterial Infections
A blood test has been developed which can rapidly tell whether a patients condition is bacterial or viral. One of the biggest implications here is in the curtailing of misuse of antibiotics, which are ineffective at combating viruses, but are often prescribed all the same. This has led to emerging bacterial strains that are resistant to all known drugs.
Overwhelming Evidence for Water on Mars
NASA’s Curiosity rover has sent back the most compelling evidence for water on Mars yet. These findings were announced at the European Planetary Science Congress which was held Sept. 8 to Sept. 13 in London. Evidence found in sedimentary rock hints at water that was both neutral and benign, and both flowing and standing in places. This is significant because standing water is an ideal place for microbes to survive and reproduce.
‘Black Holes’ Discovered at Sea
Scientists have found a mathematical equivalent to black holes in the Earth’s oceans. These large circular currents, known as eddies, are encircled by a large ring of water which forms a closed barrier around it. This is almost identical to the phenomenon -predicted by Einstein’s theory of relativity – known a light sphere. This is where a light beam no longer spirals into the black hole. Rather, it dramatically bends and comes back to its original position, forming a circular orbit.
 In case you liked what you read here but missed the last round up of fantastic news, you can check it here.
In case you liked what you read here but missed the last round up of fantastic news, you can check it here.
(Title image by t3.com)
About the author: Conor Hughes is Marketing Executive at Life Science Recruitment